introduction
3D Printing is a technique of Additive Manufacturing. Traditional manufacturing drove the industrial revolution that gave birth to our
modern society, but it has fundamental flaws that necessitate fresh approaches. (Campbell et. al)
Manufacturing is derived from the French term "manufactured by hand." However, this etymological root no longer applies to the
current condition of contemporary industrial technology. Tooling, machines, computers, and robots are all used in the complicated operations
of casting, forming, moulding, and machining. These technologies are "subtractive" techniques, in which things are formed
by
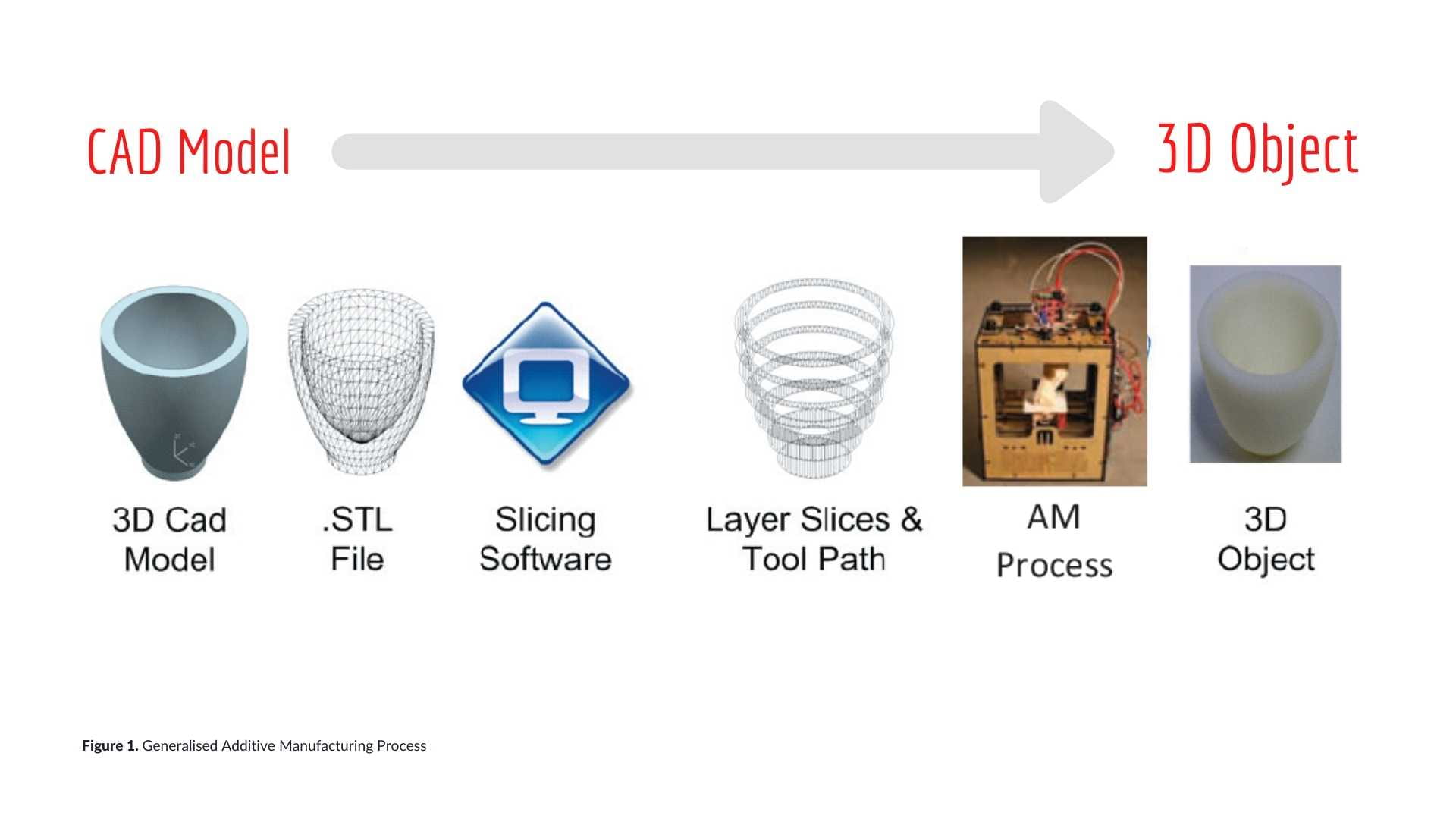
subtracting material from a workpiece, similar to a kid cutting a folded piece of paper to make a snowflake. The capabilities of the tools employed in the production processes restrict the capabilities of the final goods. Additive Manufacturing Processes, on the other hand, is a collection of new technologies that build items from the ground up by layering material one cross-sectional layer at a time. Going back to the childhood comparison, this is essentially comparable to building an object using Legos® or building blocks. Figure 1 (below) depicts the generalised phases of Additive Manufacturing technology.
PHASES OF THE
Additive Manufacturing Process
Retrocast 3D Printing provided END-to-END solutions for your concepts. Talk our team today about the realisation of your idea coming to
life. Find out how RetroCast 3D Printing can help you. Contact our team on 07
3348 5057 for
more information or Contact
Us
EXPLORING
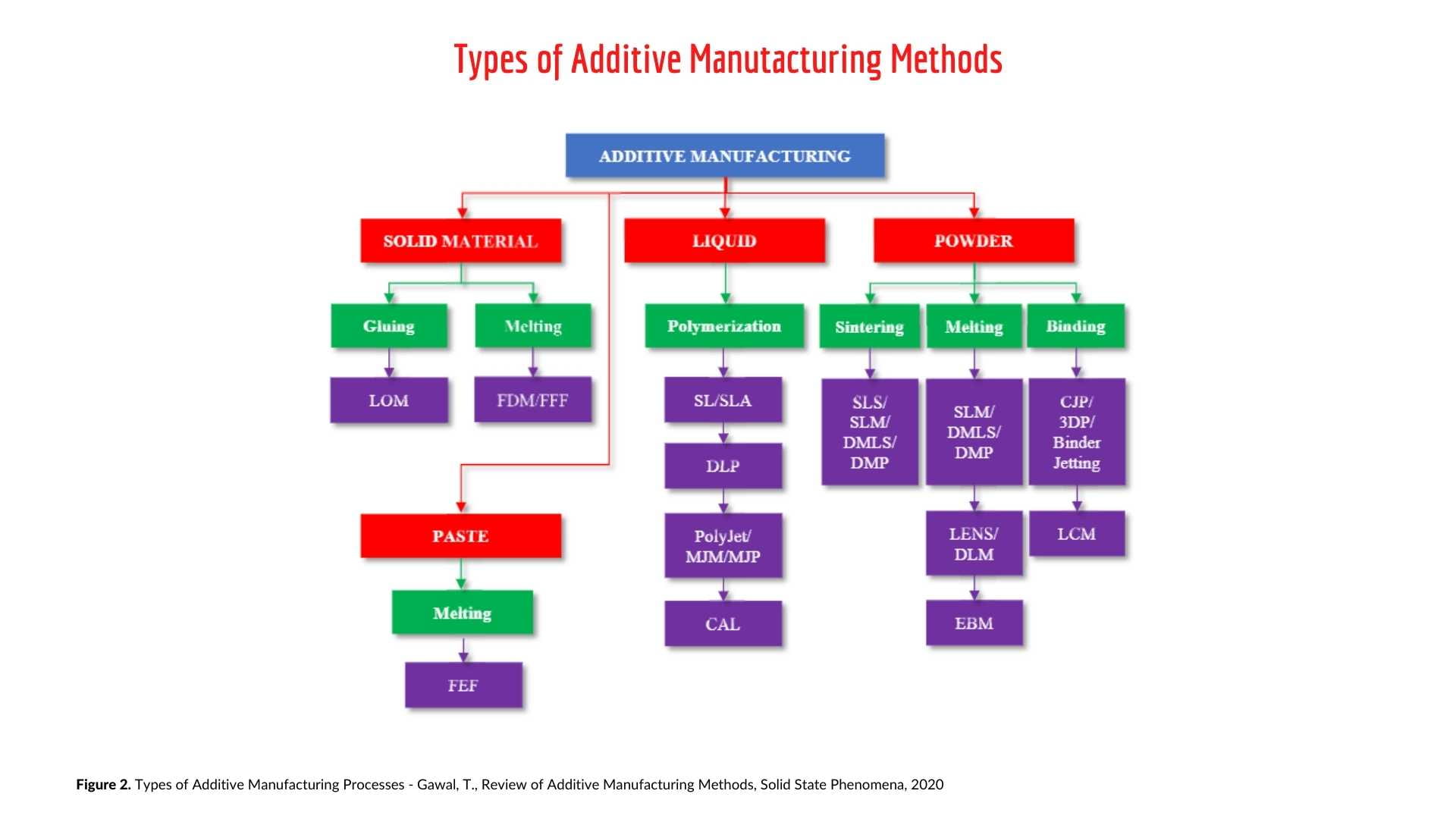
Gawal, 2020, categorises additive manufacturing processes into three main methods: processes that use Solid Material, Liquid and Powder. As shown below in Figure 2.
The three methods expand into the 7 various technical applications of these three methods as outlined below by the Additive Manufacturing
Research Group (AMRG) at Loughborough University:

Did you find what you were looking for?
source