CHUCK HALL
Thank to Chuck Hall, who invented 3D Printing, it is the future of manufacturing. The transformative impact on many industries is unimaginable. 3D printing can produce a spare part in days, introducing a positive return on investment to many sectors. This process provides the opportunity for organisations to quote for more work, turnover more products, and positively impact their bottom line.
major contributions
As described by Murray Leinster in 1945, his short story Things Pass By "., also described by Raymond F. Jones story, "Tools of the Trade," published in the November 1950 issue of Astounding Science Fiction magazine.
1971 - Liquid Metal Recorder patented by Johannes F Gottwald, a continuous Inkjet metal material device. It appears to be the first patent describing 3D printing with rapid prototyping and controlled on-demand manufacturing.
1974 - Published in Ariadne in the journal New Scientist, David E. H. Jones laid out the concept of 3D printing.
1983 - Robert Howard started R.H. Research (now called Howtek, Inc) developed a colour inkjet 2D printer called Pixelmaster, which was commercialised in 1986, using Thermoplastic (hot-melt) plastic ink.
1984 - (July), Bill Masters filed a patent for his Computer Automated Manufacturing Process and System. This filing is on record as the first 3D printing patent in history. Two weeks later than Masters, Alain Le Mehaute, Olivier de Witte, and Jean Claude André applied for the first patent on the stereolithography process.
1986 - Chuck Hull filed his patent for a stereolithography machine, which remains the most common 3D printing technique.
All metalworking was previously done by a process called non-additive manufacturing (Milling, CNC, Electrical Discharge Machinery). Automated techniques that add metal are called Additive Manufacturing.
Stanford and Carnegie Mellon University are developing techniques for micro casting and sprayed materials.
1993 Inkjet 3D printer (Sanders Prototype) called Solidscape, introduced a high-precision polymer jet fabrication system with soluble support structures (categorised as a "dot-on-dot" technique).
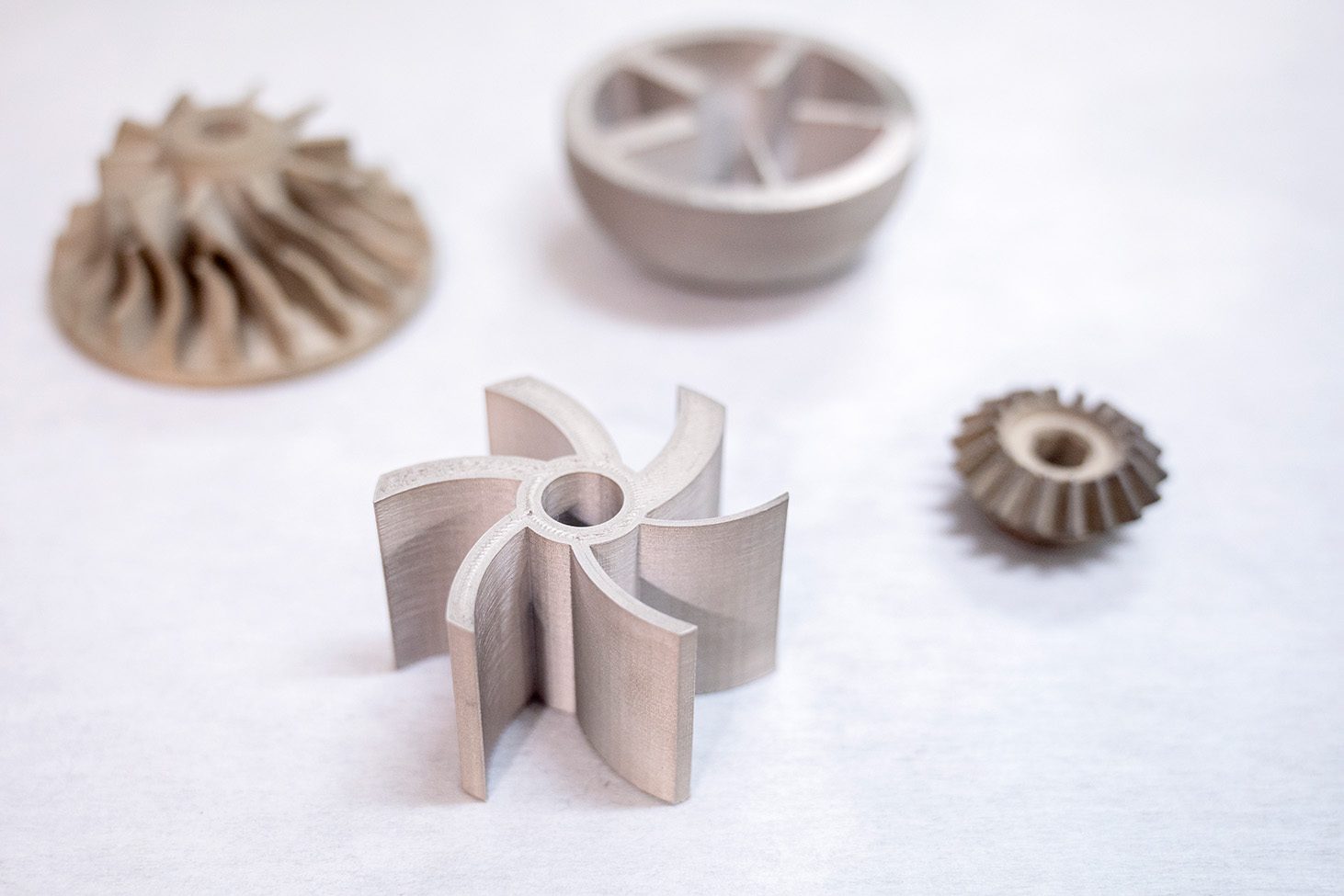
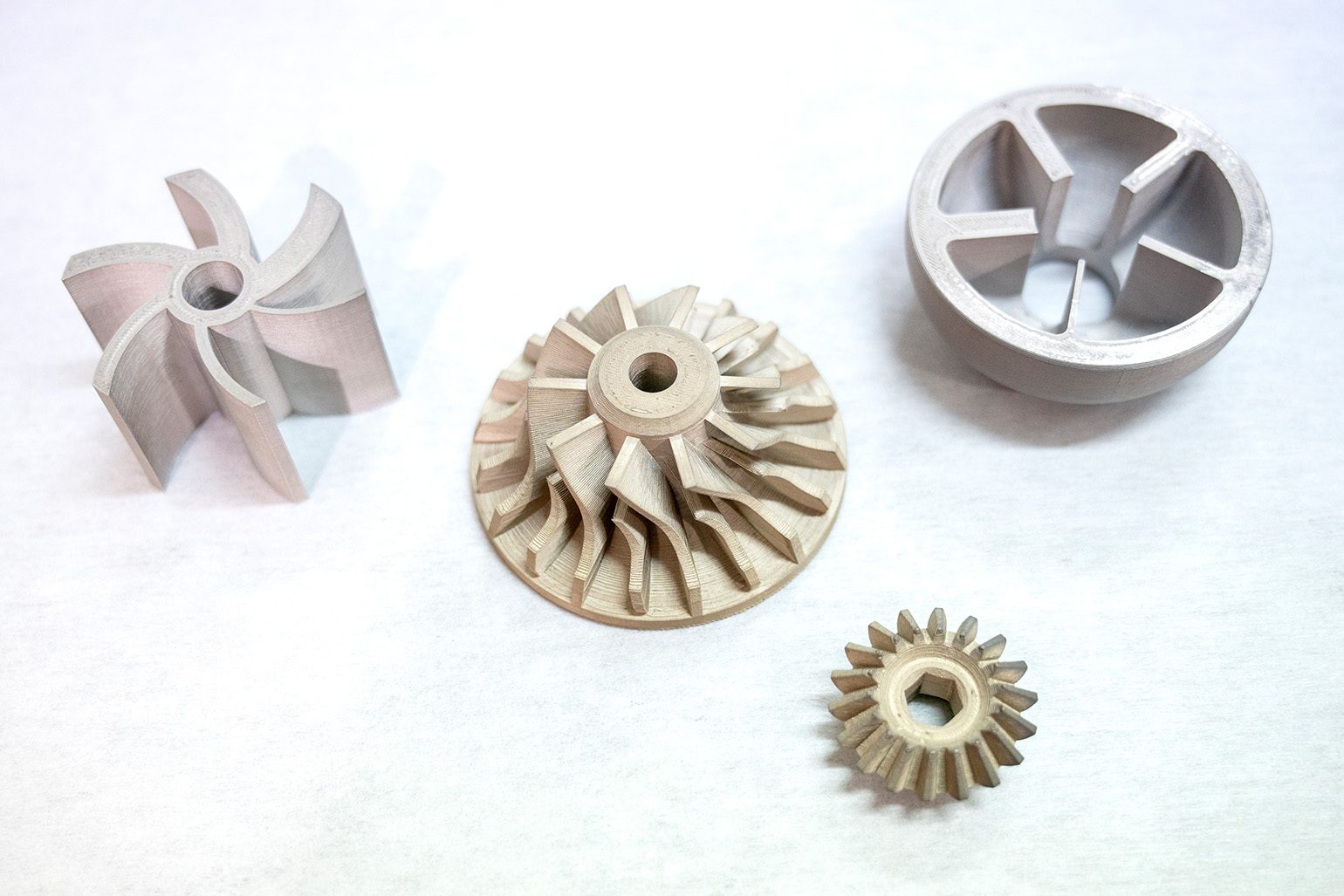
3D Printers commence printing metal end-use parts such as engine brackets and large nuts
2012 Filabot develops a process for closing the loop with plastic and allows for any Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) or Field-Flow Fractionation (FFF) 3D printer to print with a broader range of plastics.
2014 Benjamin S. Cook and Manos M. Tentzeris create a multi-material, vertically integrated printed electronics additive manufacturing platform called VIPRE, which enables 3D printing of functional electronics operating up to 40 GHz.
Find Out More About 3D Printing >
Develeopments in
Food Industry – Looking at chocolate and candy, crackers, pasta and pizza (flat foods). Nasa is also researching using this technology to reduce food waste in space.
Fashion Industry – sneakers, eyewear, on-demand clothing
Transportation – manufacturing car windscreens and windows, parts
Health - implants, kidneys, surgical sutures
Education - introducing scientific equipment to the classroom
Cultural heritage - recreating missing pieces of relics
Additive manufacturing is now 33 years old and represents a market with annual growth of 20 and 30%. Today, additive manufacturing is experiencing great innovation in its processes, software, manufacturing, and materials used.
As a result, the limitations of the process have begun to emerge, which includes the quality of the tools, their cost of manufacture, the multi-material aspects, functionalities, and surface conditions.

Conceptually having a tangible object can help you through the creative process. Retrocast 3D Printing will construct concept models that
mimic the appearance of production-run parts.
Learn More

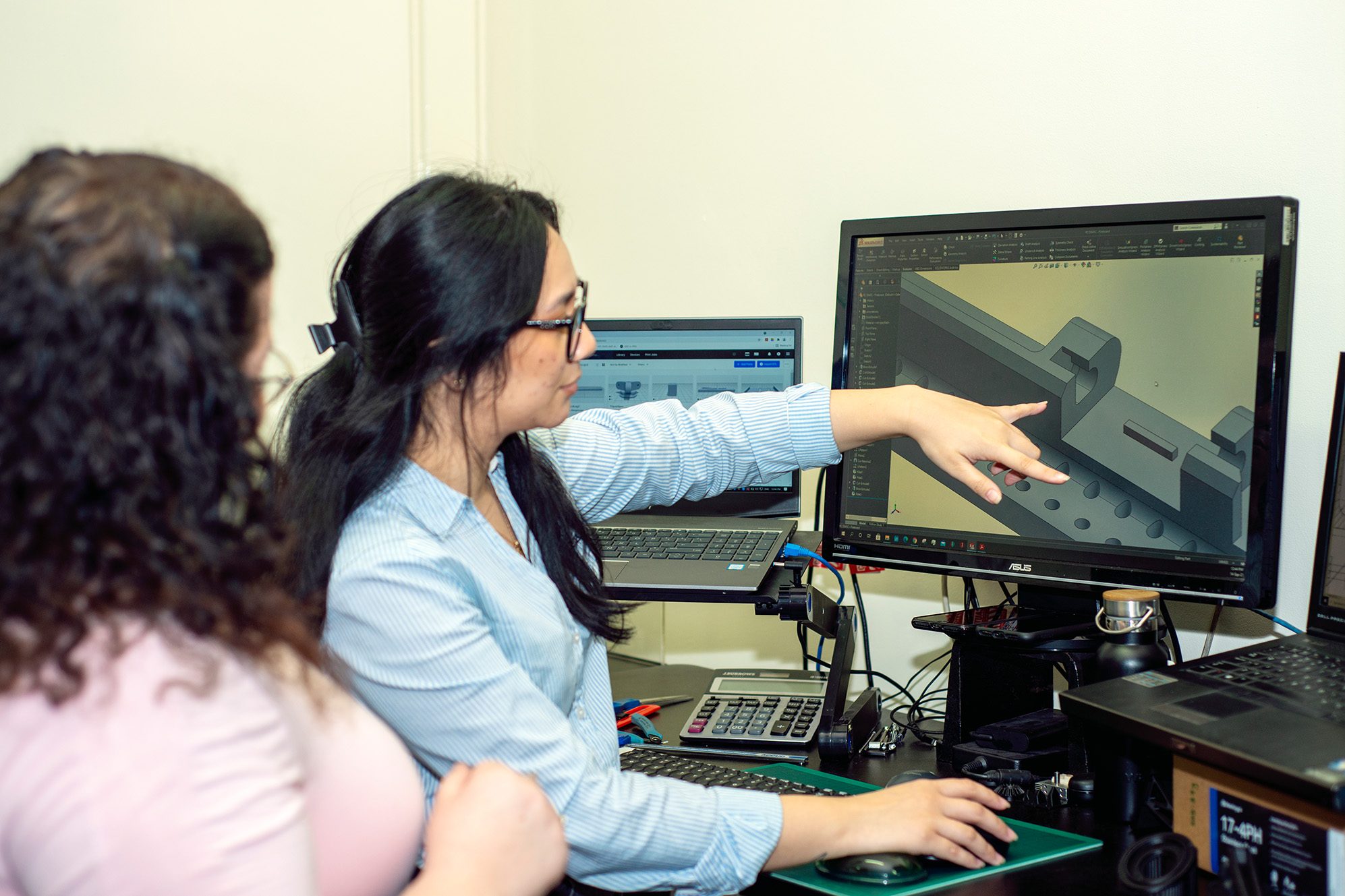
Display your design and relay the marketability of
your product. Create a market for your product before production. Send your 3D Concept to Retrocast 3D Printing to explore your
options and get a quote.
Get a Quote
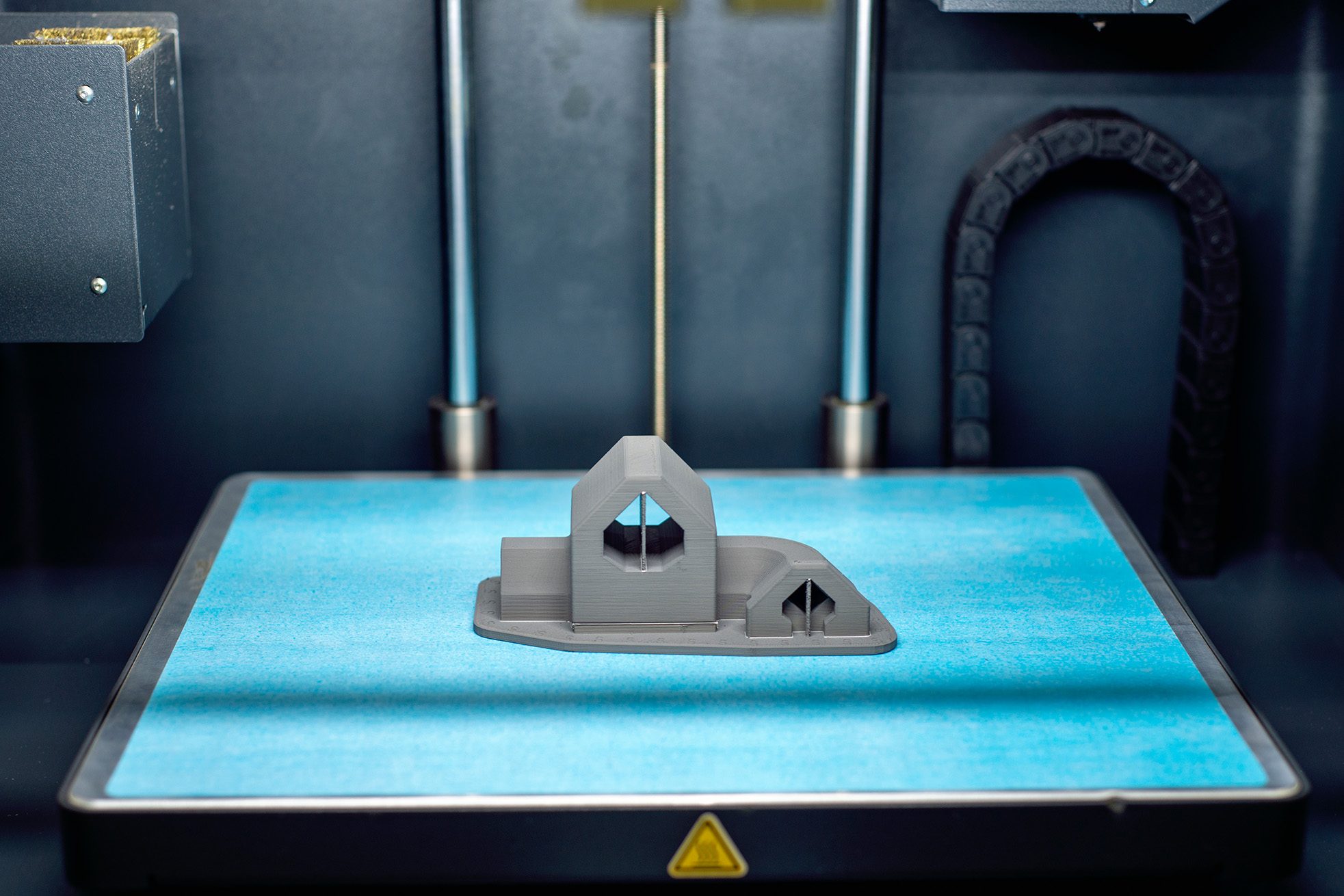
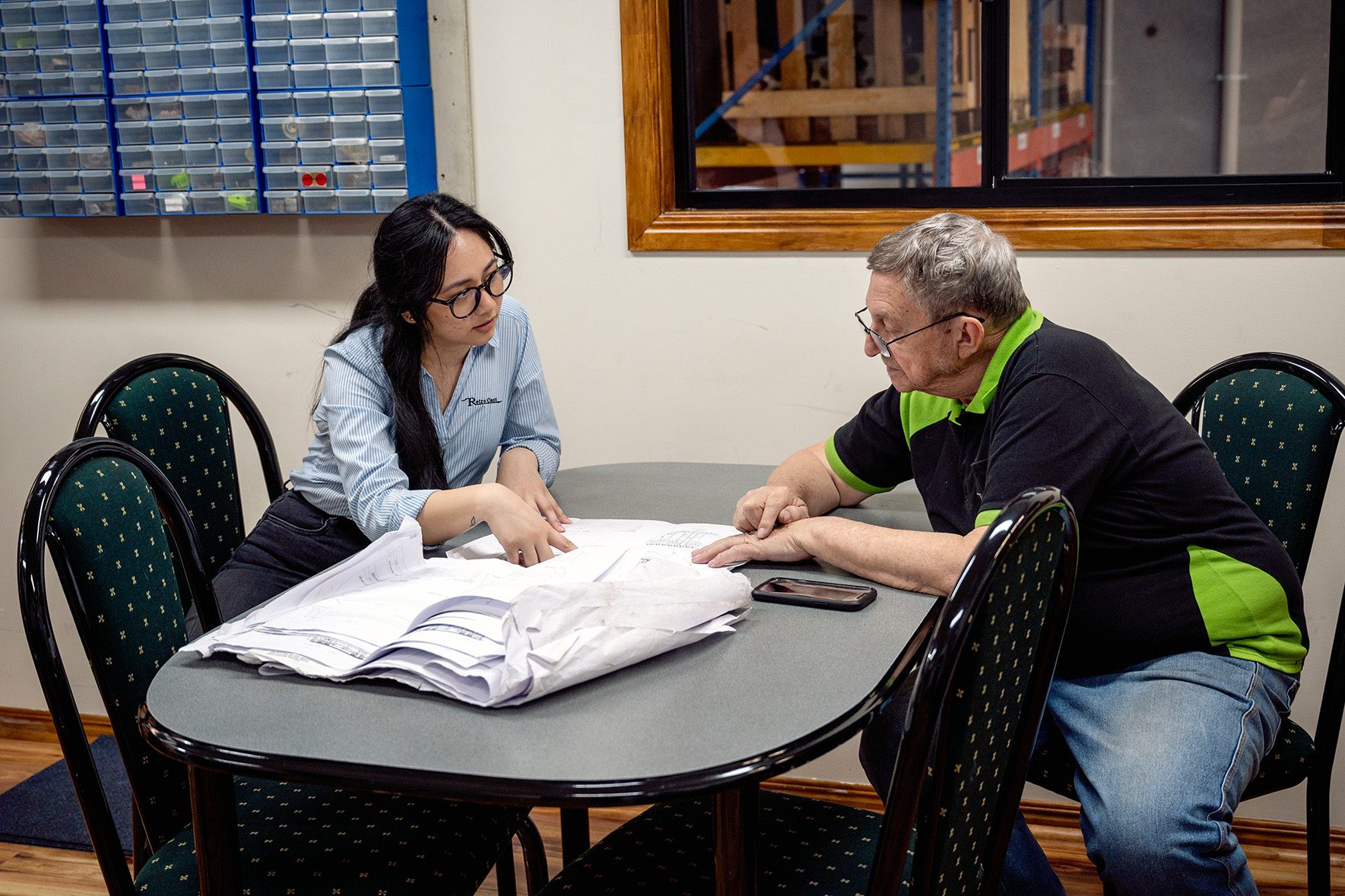
We can test your new product is doable prior to full production. Rapid prototyping services allows us to test the form, fit, and function of your prototype.
Ensuring durability and quality.
Discover More
SOURCES
J.-C. André (Jean-Claude), ; 2017 ; 1st edition.